TONGUE-TIES
+ Tethered Oral Tissues

TONGUE + LIP TIES
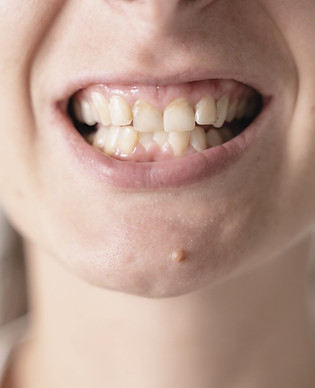
Tongue-ties and lip-ties, collectively known as tethered oral tissues, are often misunderstood and misdiagnosed, even though they are quite common. These issues can have profound effects on various aspects of health and development.
TLDR: guide for Kids and Parents on the Impacts of Tongue-Tie
Tongue-tie can lead to open-mouth breathing, which can dry out and irritate the soft tissues in the mouth and throat, potentially causing inflammation of the tonsils and airway blockage. Additionally, tongue-tie can force the tongue to rest in a lower position, hindering proper palate development, resulting in smaller nasal passages and sleep-disordered breathing.
A frenectomy/frenuloplasty, a procedure to revise tongue or lip ties, can help alleviate these issues, particularly when performed during infancy using a dental CO2 laser for minimal discomfort and faster healing.
Healthy Development:
Tongue-Tie + Beyond
Releasing tongue-ties, especially in infancy, can lead to better breastfeeding outcomes, improved comfort for mothers, and more efficient sucking for babies. Breastfeeding can help broaden the palate and increase nasal cavity size, potentially preventing future airway issues. Additionally, early introduction of solid foods through baby-led weaning encourages proper jaw development, reducing the risk of malocclusion and the need for orthodontics.



How the Tongue is tied to overall wellness
The tongue is far too often often under-appreciated as a key to wellness, impacting sleep, breathing, speech, feeding, and facial development. Its position during sleep is vital to keep airways open and reduce sleep apnea risk.
More than just a taste organ, the tongue is a complex system of muscles that grant us the ability to move food around in the mouth when eating and swallowing.
When it comes to breathing, it regulates airflow, essential for the body's oxygenation.In speech, the tongue's agility enables sound articulation and clear communication. It also shapes facial growth in children, affecting oral health.